The proteostasis network of heat shock proteins The heat shock Biology Diagrams Heat shock is caused by fever and inflammation in the human body and an increased temperature of the surrounding environment, which induces protein aggregation and misfolding [1].Heat shock prompts cellular reactions, such as cell death, cell cycle arrest, and protein degradation by eliciting DNA damage response, changing in cell membrane fluidity, and disorganizing of cytoskeletal proteins This behavior clearly suggests a lasting problem connected with mitosis. Heat shock is known to induce replication-dependent DNA damage and the phosphorylation of the H2AX histone Heat Shock Targets the Distribution of RNA Binding Proteins in Mitosis. The behavior of RNA binding proteins and ribonucleoprotein complexes at mitosis is still Heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) is a molecular chaperone involved in folding, assembly, maturation, and stabilization of the client proteins that regulate survival of malignant cells. -M phase and entered aberrant mitosis in a BRCA1-dependent manner. Failure to arrest the cells at or before mitosis resulted in formation of micronucleated

Background: Nucleolin is an RNA-binding protein that regulates RNA stability. Results: CDK1 phosphorylates nucleolin at Thr-641/707 to stabilize nucleolin in a heat shock protein 90-dependent manner. Conclusion: Nucleolin stabilized by Hsp90 contributes to lung tumorigenesis by increasing the level of many tumor-related mRNAs during mitosis. Significance: Cancer cells exploit the increase in
Heat Shock Affects Mitotic Segregation of Human Chromosomes Bound to ... Biology Diagrams
Heat shock protein (Hsp) 90, a constituent molecular chaperone, is an abundant protein comprising 2% of the total cellular protein content under nonstress conditions. Therefore, the chaperone Hsp90 is very important for maintaining the stability of the nuclear proteins during mitosis. Materials and Methods Materials. Polyclonal antibodies

Hsp105 prevents abnormal cell division by contributing to SAC activation under heat shock and nonstressed conditions by interacting with Cdc20 but not affecting formation of the mitotic checkpoint complex.-Kakihana, A., Oto, Y., Saito, Y., Nakayama, Y. Heat shock-induced mitotic arrest requires heat shock protein 105 for the activation of Known as the primary regulators of the evolutionarily conserved Heat Shock Response defense mechanism, activated HSFs trimerize and drive the expression of genes in response to protein-damaging The dwell time curves for Halo-H2DBD reveal that the truncation is less dynamic in both interphase and mitosis than the full-length protein,

Mitotic catastrophe cell death induced by heat shock protein 90 ... Biology Diagrams
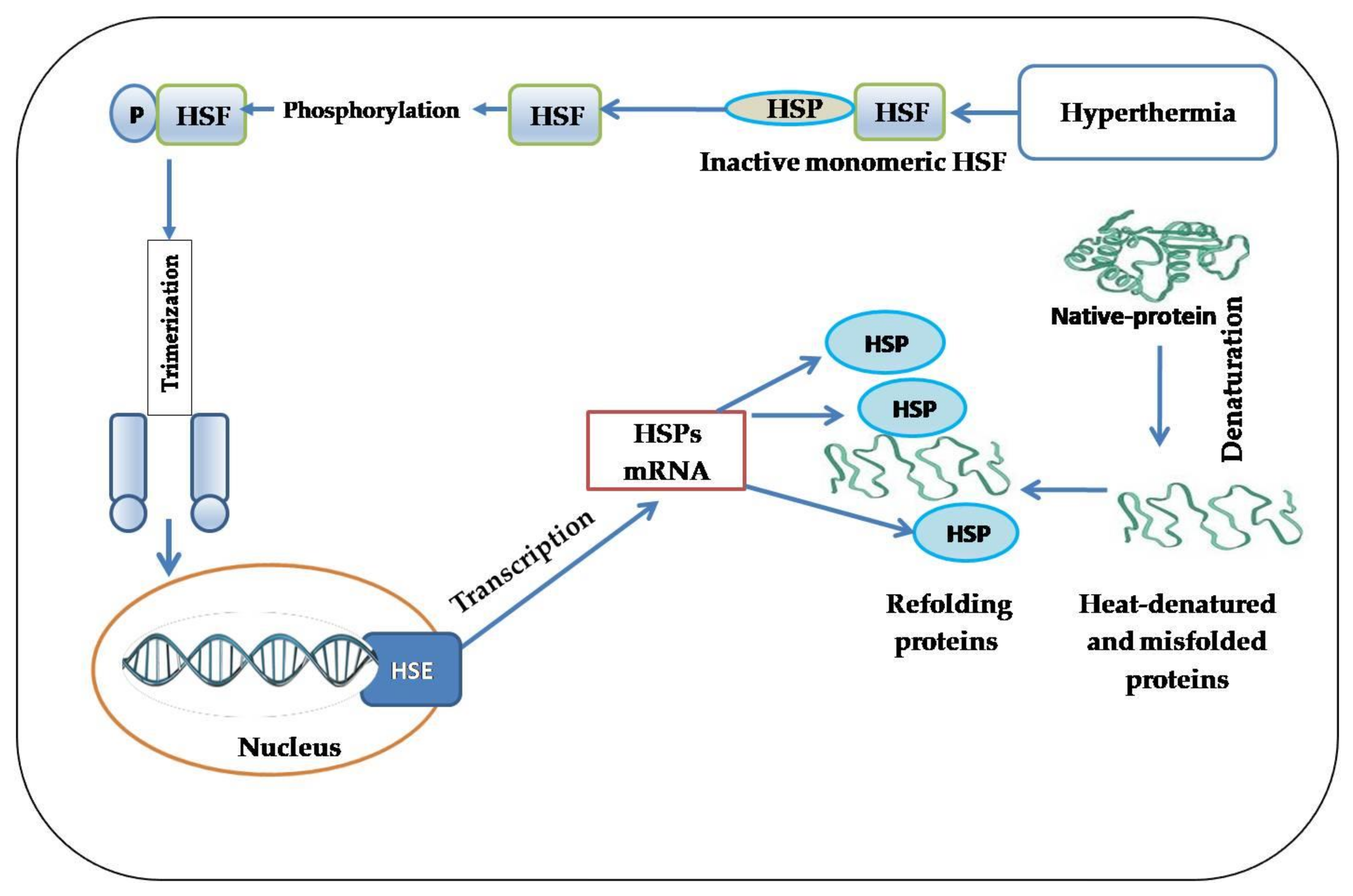
The main molecular event after heat shock is denaturation and subsequent aggregation of proteins. Expression of heat shock proteins can protect the cells from these effects (Fischer et al., 2002). The recruitment of Hsp70 after heat shock to centrosomes, but not to microtubules or kinetochores, suggests that such heat-induced protein damage