Understanding bone density tests can help prevent further problems Biology Diagrams Bone density refers to the amount of mineral matter per square centimeter of bones, indicating their strength and structural integrity. This measurement is crucial in understanding bone health, as higher bone density generally correlates with stronger bones that are less susceptible to fractures and diseases such as osteoporosis. Factors influencing bone density include genetics, age Bone mass accounts for 50 to 70% of bone strength . Bone geometry and composition are important, however, because larger bones are stronger than smaller bones, even with equivalent bone mineral density. As bone diameter expands radially, the strength of bone increases by the radius of the involved bone raised to the fourth power. Bone anatomy Skeletal function. Our skeletons are responsible for several important mechanical and non-mechanical functions[22,36,87]. Isolehto J, Alén M, Kiviranta I, et al. Bone density, structure and strength, and their determinants in aging sprint athletes. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2012;44(12):2340-9. doi: 10.1249/MSS.0b013e318267c954.
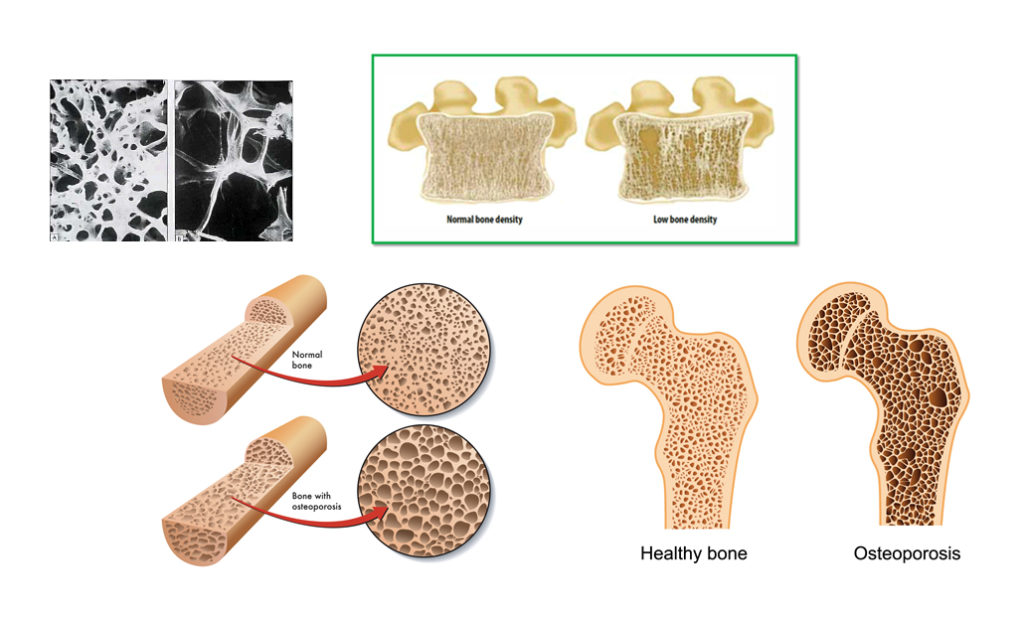
Bone density is a measure of the amount of minerals (mainly calcium and phosphorous) contained in a certain volume of bone, accounting for approximately 60% of bone strength. Bone density changes throughout life. Bone mineral density (BMD) is set by the amount of bone present in the skeletal structure; the higher the BMD, the stronger the bones, and vice-versa. BMD is greatly influenced by The adult human skeleton is composed of 206 bones. At birth, there are approximately 270 bones, with the final adult count decreasing as a portion of these bones fuse during phases of skeletal growth and maturation. Bone is a metabolically active connective tissue that provides structural support, facilitates movement, and protects vital organs; this tissue plays an important role in

Bones: Anatomy, function, types and clinical aspects Biology Diagrams
Anatomy - Bone Density. Flashcards; Learn; Test; Match; Q-Chat; Get a hint. skeleton functions. support body and muscles, movement (muscle attaches to bone), protection (enclose organs), blood formation from red bone marrow, electrolyte balance (calcium, phosphate reservoir), acid base balance (bone buffers blood excess pH change w/ alkaline A bone is a somatic structure that is composed of calcified connective tissue. Ground substance and collagen fibers create a matrix that contains osteocytes.These cells are the most common cell found in mature bone and responsible for maintaining bone growth and density. Within the bone matrix both calcium and phosphate are abundantly stored, strengthening and densifying the structure. A scanner used to measure bone density using dual energy X-ray absorptiometry. Bone density, or bone mineral density, is the amount of bone mineral in bone tissue.The concept is of mass of mineral per volume of bone (relating to density in the physics sense), although clinically it is measured by proxy according to optical density per square centimetre of bone surface upon imaging. [1]

